
#Lattice energy equation ke free
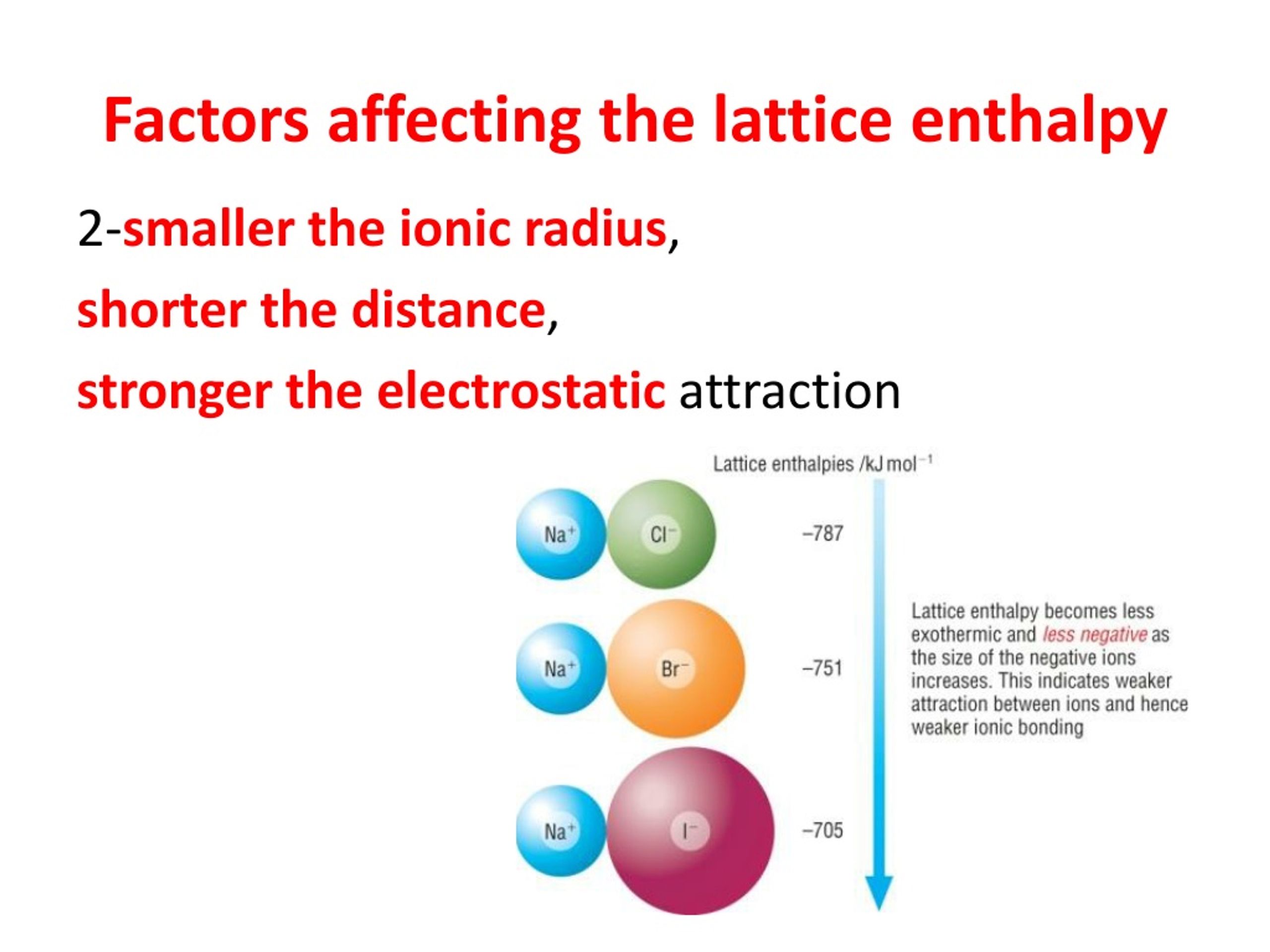
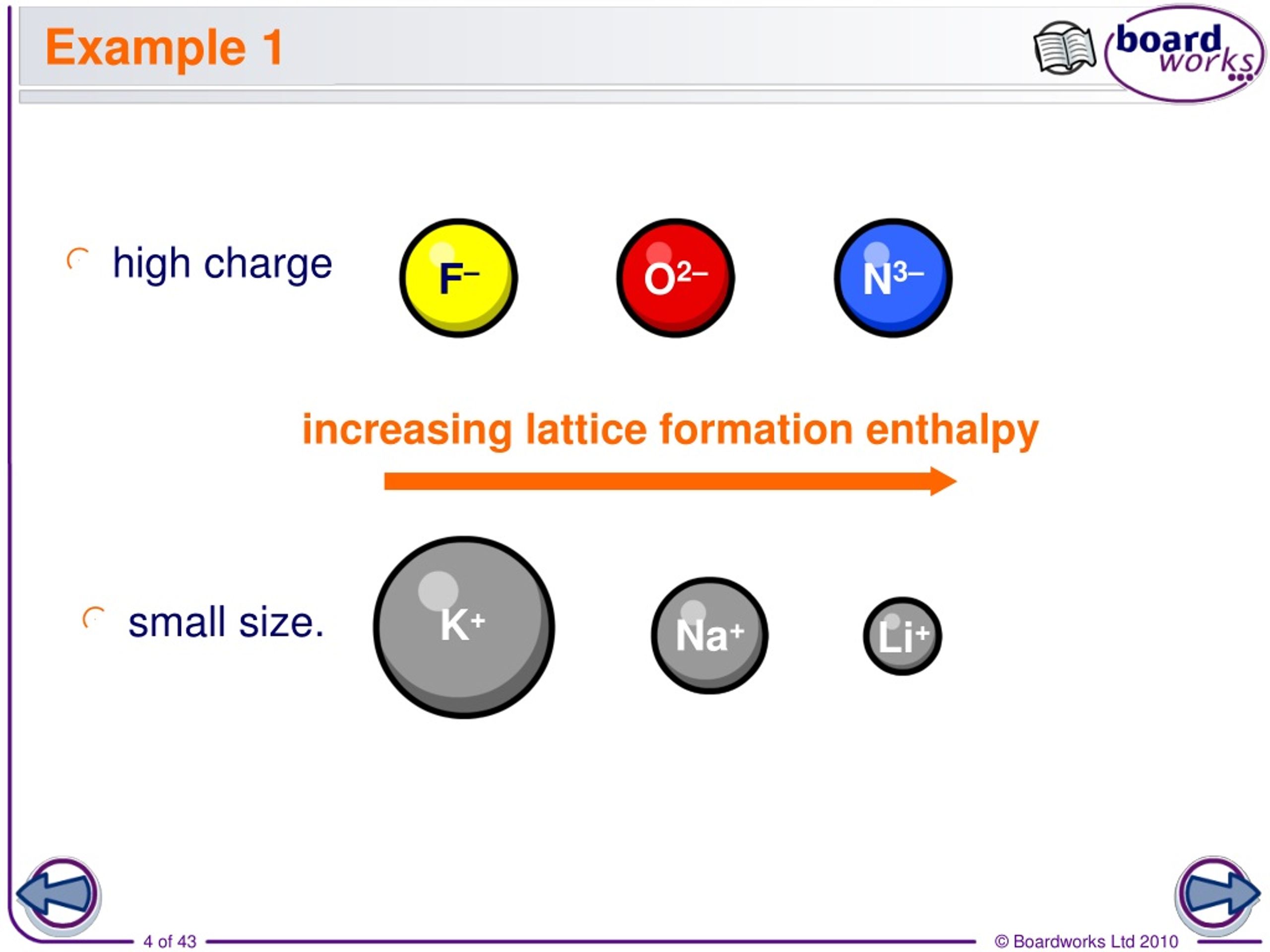
Ulattice NAMz+ze2 40r0 (1 1 n) U l a t t i c e N A M z + z e 2 4 0 r 0 ( 1 1 n) Where. Electrostatic potential Epair 2 2 40 z magnitude of charge on each ion e electronic charge 1.6 × 1019 C 0 permittivity of free space (40 1.112 × 1010 C2/J.m) r distance between two oppositely charged ions EA 2 2 40. We can calculate the lattice energy of any ionic solid rather accurately by using a modified form of Coulomb’s law as shown below. Lattice energy can be calculated from the Born-Lande equation which is derived from the electric potential of the ionic lattice and repulsive potential energy. Fig.3 We can treat the motion of this lattice in a similar fashion as for monoatomic lattice. Fig.3 shows a diatomic lattice with the unit cell composed of two atoms of masses M1 and M2 with the distance between two neighboring atoms a. The attraction of the two ions releases energy and the process is exothermic. Ionic Charge – The lattice energy gets more exothermic as the ionic charge of the ions increases and we know that the greater the ionic charge, the higher the charge density.This results in a stronger electrostatic attraction between the oppositely charged ions in the lattice and in turn, the lattice energy is more exothermicįormula to Calculate the Lattice Enthalpy. that the diatomic lattice exhibit important features different from the monoatomic case. Lattice energy can be a very complicated process but is often simplified by using Coulombs law.The ions are also further apart from each other in the lattice. Ionic Radius – The lattice energy becomes less exothermic as the ionic radius of the ions increases because the charge on the ions is more spread out over the ion when the ions are larger. There are several different equations, of various degrees of complication, for calculating lattice energy in this way.

Other values for other structural types are given in Table 6.13E. This type of energy cannot be measured empirically, but can be calculated using electrostatics or estimated using the Born Haber cycle and its units are kJ/mol. The Madelung constant depends on the structure type and Equation 6.13E.10 6.13E.10 is applicable only for the sodium chloride (ei.g, rock salt) lattice geometry. It is based on Coulomb’s law, which states that the attractive or repulsive force between two charged particles is directly proportional to the product of their charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Element X reacts with sodium to form an ionic compound with the formula Na2X. In the present work it was shown that low lattice energy ammonium salts are not favorable for polymer electrolyte preparation for electrochemical device applications. The Coulombic equation is a commonly used formula for calculating the lattice energy of an ionic compound. Lattice energies are important in predicting the solubility and stability of ionic solids in water. Because of their smaller size and higher charge, the hydration energies of. S5: the whole phonon dispersions of Mg 3 Sb 2 at 300 K and 700 K. For the reverse process of Equation 1: aMb+(g) + bXa(g) MaLb(s) the energy released is called energy of crystallization ( Ecryst ). Lattice energy U L per mole may be defined as the sum of the electrostatic and repulsive energy. As defined in Equation 1, the lattice energy is positive, because energy is always required to separate the ions. The total potential energy of the ionic compounds is also referred as the lattice energy.

5-13) to calculate the lattice energy of MgF2 using these thermodynamic. Lattice energy refers to the energy which is released while two oppositely charged gaseous ions attract to each other and form an ionic solid. Problem 96QRT: Use a Born-Haber cycle (Sec. Compare your answer to the experimental lattice energy of -1971 kJ/mol. Lattice energy also known as lattice enthalpy required to separate a mole of an ionic solid into gaseous ions or the energy that must be supplied to one mole of an ionic crystal in order to separate it into gaseous ions in a vacuum via an endothermic process. A Magnesium atom loses Calculate the lattice energy of Magnesium Sulfide from the. Determine the theoretical lattice energy using the Kapustinskiis equation 1.202 x 105 VZZ° U 34.5 r + r- r + r Ca2+ 114 pm I 206 pm b.
#Lattice energy equation ke how to
\( \newcommand\)).Ahead of discussing how to calculate lattice energy, let’s define it.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
